Forex trading is a popular form of investing that involves the buying and selling of currency pairs in order to make a profit. However, it is important to understand the various terms and concepts involved in forex trading in order to be successful. One such term is “swap”, which is a common aspect of Forex trading. In this article, we will explore what swap means in forex, and why it is an important consideration for traders.
The impact of swap rates on a trader’s overall profit or loss can be significant, especially for long-term trades [1]. Therefore, it is important for traders to consider swap rates when entering into trades, and to factor them into their overall trading strategy. In addition, some forex brokers may offer swap-free accounts, which are designed to help traders avoid paying or receiving swap fees.
Overall, understanding what swap means in forex is an important aspect of successful trading. By considering swap rates and incorporating them into their trading strategy, traders can make informed decisions and increase their chances of profitability in the forex market.
What Does Swap Mean in Forex?
Swap rates are typically quoted in pips, which is the smallest unit of measurement in forex trading. For example, if the swap rate for the EUR/USD currency pair is 0.5 pips, this means that the trader will earn or pay 0.5 pips for each day that the trade is held overnight [2]. It is important to note that swap rates can be either positive or negative, depending on the interest rate differential between the two currencies.
Types of Swaps:
Fixed-For-Floating Rate Swap
In this type of swap, two parties agree to exchange cash flows based on different interest rates. One party agrees to pay a fixed interest rate, while the other agrees to pay a floating interest rate. For example, one party may agree to pay a fixed interest rate of 4%, while the other party agrees to pay a floating interest rate based on the LIBOR rate [3]. The two parties then exchange the cash flows based on the agreed-upon terms.
Fixed-For-Fixed Rate Currency Swap
In this type of swap, two parties agree to exchange cash flows based on different currencies and fixed interest rates. For example, one party may agree to pay a fixed interest rate of 5% on a US dollar loan, while the other party agrees to pay a fixed interest rate of 6% on a euro loan. The two parties then exchange the cash flows based on the agreed-upon terms, with each party receiving the other’s cash flow in their own currency. This type of swap is often used by companies to manage their currency and interest rate exposure.
Reasons for Using Currency Swaps:
Decreasing Borrowing Costs
Currency swaps can be used to reduce borrowing costs by allowing companies to access cheaper financing in foreign currencies.
For example, if a company wants to borrow money in the US but finds that US interest rates are too high, it can enter into a currency swap agreement with a counterparty that can borrow money at a lower interest rate in another currency.
The company can then exchange the cash flows, allowing it to borrow money at a lower overall cost [4].
Reducing Exchange Rate Risks
Currency swaps can also be used to reduce exchange rate risks by allowing companies to lock in exchange rates for future transactions.
For example, if a company expects to receive payment in a foreign currency at a future date, it can enter into a currency swap agreement to lock in the exchange rate, reducing the risk of fluctuations in the exchange rate affecting the value of the payment. This can be particularly useful for companies with significant international transactions or exposure to multiple currencies.
When Are Swaps Charged?
Swaps are charged or paid based on the net open positions held by a trader at the end of each trading day. The specific time at which swaps are charged may vary depending on the broker or trading platform being used, but generally, swaps are charged at the end of each trading day, which is usually at 5 pm Eastern Standard Time (EST) in the United States [1].
The swap fee is charged or paid based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded, and it reflects the cost of holding a position overnight. If the interest rate of the currency being bought is higher than the interest rate of the currency being sold, the trader will receive a positive swap, meaning they will earn interest on the position held overnight.
On the other hand, if the interest rate of the currency being sold is higher than the interest rate of the currency being bought, the trader will receive a negative swap, meaning they will pay interest on the position held overnight.
How Can You Calculate the Swap Rate?
When trading forex, a swap is a fee charged for holding a position overnight. The swap rate is the interest rate differential between two currencies and is calculated based on the interest rates of the currencies involved.
There are different ways to calculate the swap rate, depending on the broker and the trading platform. In general, the swap rate is calculated using the following formula [6]:
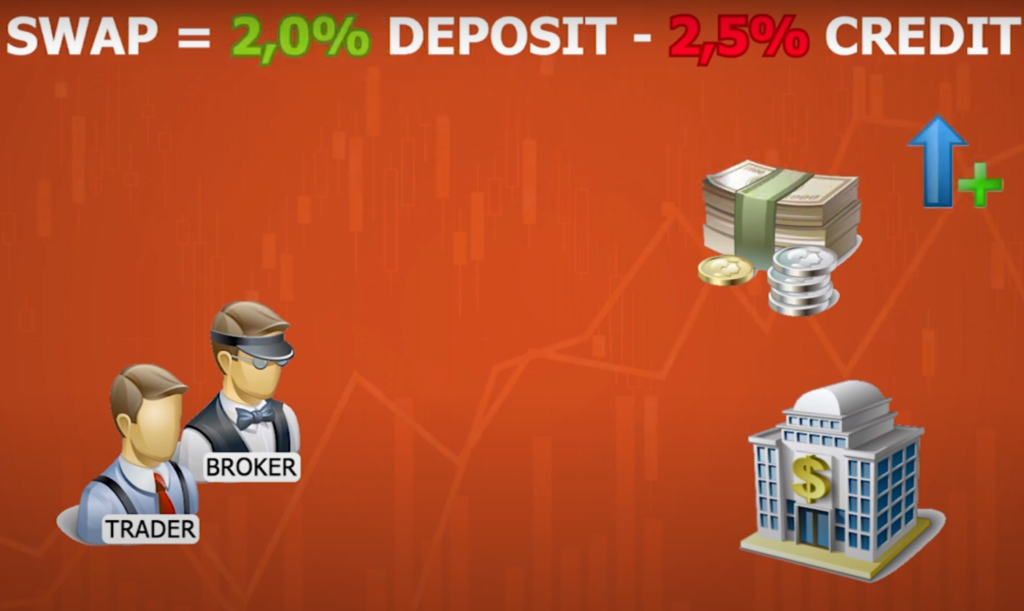
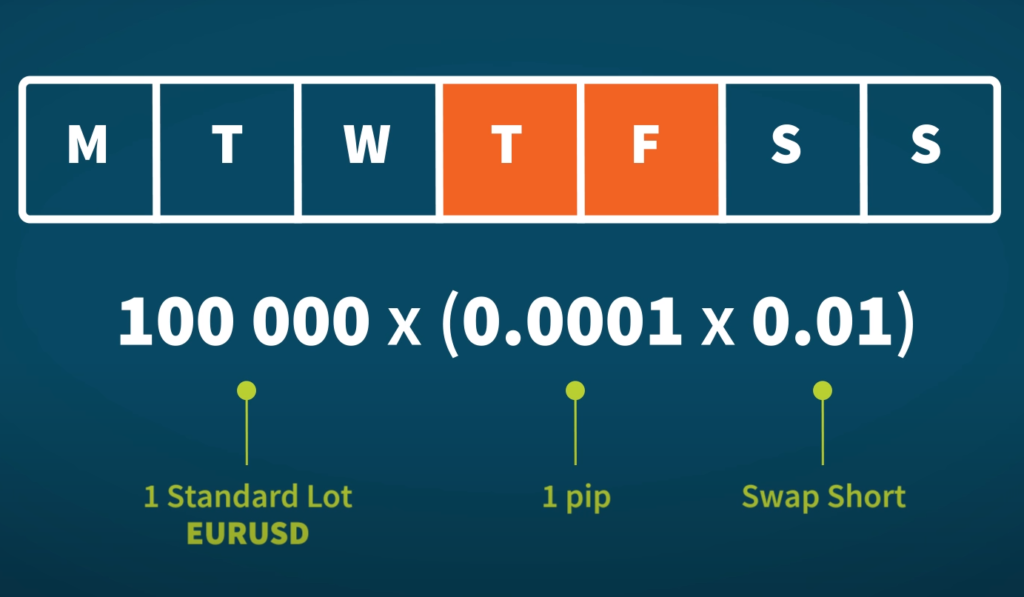
Swap Rate = (Interest Rate of the Currency You Are Buying – Interest Rate of the Currency You Are Selling) x Notional Value x Swap Rate in Percentage / 100
Here is a breakdown of the variables in the formula:
- Interest Rate of the Currency You Are Buying: This is the interest rate of the currency you are buying, as determined by the central bank of the country issuing the currency;
- Interest Rate of the Currency You Are Selling: This is the interest rate of the currency you are selling, as determined by the central bank of the country issuing the currency;
- Notional Value: This is the value of the position you are holding in the currency pair, measured in the base currency;
- Swap Rate in Percentage: This is the percentage rate charged by the broker for holding the position overnight. The swap rate can be either positive or negative, depending on the interest rate differential and the direction of the trade;
Let’s take an example to illustrate the calculation of the swap rate. Suppose you are holding a long position in EUR/USD, and the interest rate of the euro is 0.05%, while the interest rate of the US dollar is 1.25%.
The notional value of your position is $ 100,000, and the swap rate charged by your broker is -0.5%:
- Swap Rate = (0.05% – 1.25%) x $ 100,000 x (-0.5%) / 100
- Swap Rate = (-1.20%) x $ 100,000 x (-0.5%) / 100
- Swap Rate = $ 6.00
In this example, the swap rate is $ 6.00, which means that you will be charged $ 6.00 for holding the position overnight. If the swap rate were positive, you would earn money for holding the position overnight.
It is important to note that the swap rate is not a fixed amount and can change based on market conditions and the policies of central banks. Traders should always check with their brokers for the latest swap rates and factor them into their trading strategies.
Additionally, traders should be aware of the potential impact of swap rates on their trading costs and profits and should consider using swap-free accounts or other strategies to reduce their swap fees.
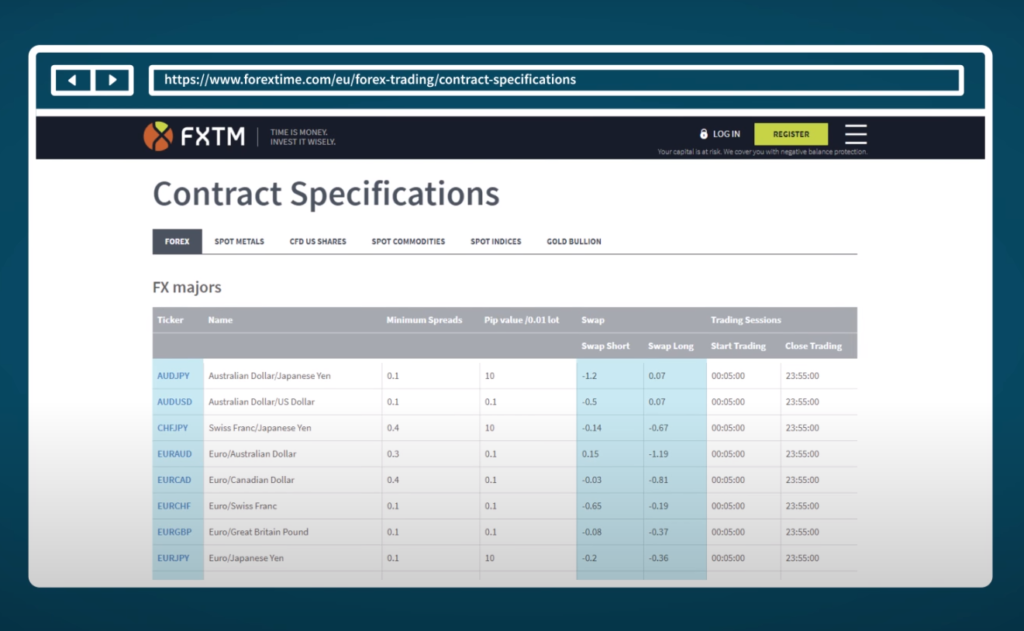
Swap Rates in MetaTrader 5
MetaTrader 5 is a popular trading platform used by forex traders around the world. The platform offers a range of features and tools to help traders analyze the market and execute trades. One of the features of MetaTrader 5 is the ability to view and calculate swap rates for forex trades [7].
To view swap rates in MetaTrader 5, follow these steps:
- Open the Market Watch window by clicking on the “View” menu and selecting “Market Watch” or by pressing “Ctrl + M” on your keyboard;
- Right-click on the currency pair you are interested in and select “Symbols” from the drop-down menu;
- In the “Symbol” window, select the “Specification” tab;
- Scroll down to the “Swap Long” and “Swap Short” columns to view the swap rates for long and short positions, respectively;
The swap rates displayed in MetaTrader 5 are calculated based on the interest rate differentials between the two currencies in the currency pair and the swap rate charged by the broker. The rates are updated regularly to reflect changes in market conditions and central bank policies.
In addition to viewing swap rates in MetaTrader 5, traders can also use the platform to calculate the swap rate for a specific trade.
To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the “Trade” tab in the Terminal window by clicking on the “Trade” button or by pressing “Ctrl + T” on your keyboard;
- Right-click on the trade you want to calculate the swap rate for and select “Properties” from the drop-down menu;
- In the “Trade” window, select the “Symbol” tab;
- Check the “Use Custom Values” box and enter the swap rate charged by your broker in the “Swap Long” and “Swap Short” fields;
- Click “OK” to save the changes;
- Once you have entered the swap rate, MetaTrader 5 will calculate the swap for the trade and display it in the “Trade” tab in the Terminal window;
Why Do Companies Do Foreign Currency Swaps?
Companies engage in foreign currency swaps to manage their currency risk and reduce their exposure to fluctuations in exchange rates. Currency risk arises when a company has assets, liabilities, or transactions denominated in a foreign currency, which exposes the company to the risk of exchange rate fluctuations.
Foreign currency swaps allow companies to exchange cash flows or assets denominated in one currency for those denominated in another currency, effectively hedging against currency risk. For example, a company with a liability in USD may swap this liability for liability in EUR with a bank or another counterparty. This effectively locks in the exchange rate between the two currencies, protecting the company from adverse movements in the exchange rate [8].
Companies may also use foreign currency swaps to manage their cash flow and funding needs. For example, a company may need to raise funds in a foreign currency to finance an overseas project or investment. By entering into a currency swap, the company can effectively borrow in the foreign currency and convert the cash flows back into their domestic currency, reducing their exposure to exchange rate fluctuations.
Foreign currency swaps are also commonly used by multinational companies to manage their currency exposure across different subsidiaries or operations. By using currency swaps, companies can effectively balance their currency exposure and manage their risk effectively.
What Is Swap Fee In Forex Islamic Accounts?
Swap fees are charges that are applied to forex trades held overnight. In conventional forex trading accounts, these fees are charged to the account for the difference in interest rates between the two currencies in a currency pair.
However, for traders who follow the Islamic faith, paying or receiving interest is forbidden, as it is considered to be riba (usury) [9]. As a result, Islamic forex accounts were created to allow traders to comply with Islamic principles while participating in the forex market. These accounts are also known as swap-free or Shariah-compliant accounts.
In Islamic forex accounts, swap fees are replaced by an administration fee or commission, which is typically charged as a percentage of the trade value. This fee is designed to cover the costs incurred by the broker for maintaining the trade overnight, without charging or paying interest.
The administration fee is usually a fixed percentage of the trade value, and it is applied to both long and short positions held overnight. This means that traders who hold their trades open overnight in an Islamic forex account do not incur any interest charges or swap fees, but they will have to pay an administration fee or commission instead.
It is important to note that not all brokers offer Islamic forex accounts, and the terms and conditions may vary depending on the broker. Traders who are interested in opening an Islamic forex account should carefully review the terms and conditions, including the administration fee or commission charged by the broker.
Who Would Use a Swap?
Swaps are commonly used by a variety of participants in the forex market, including traders, investors, corporations, and central banks.
Swaps can also be used to hedge against currency risk, such as when a trader needs to hold a position in a currency but does not want to be exposed to the currency’s exchange rate fluctuations.
Investors may also use swaps to earn a return on their investments. For example, an investor might invest in a bond denominated in a foreign currency, earning both the bond’s interest payments and the interest rate differential between the foreign currency and their domestic currency.
Corporations may use swaps to manage their currency risk, such as when they have operations in multiple countries and need to manage their exposure to currency fluctuations. For example, a multinational corporation might use a currency swap to convert a loan denominated in one currency into another currency to hedge against exchange rate risk [10].
Central banks may also use swaps to manage their foreign currency reserves and stabilize their currency’s exchange rate. For example, a central bank might engage in a currency swap with another central bank to borrow foreign currency, allowing it to intervene in the forex market and stabilize its currency’s value.
Can I Make Money From Swap In Forex Trading:
Carry Trade
The carry trade strategy is one of the most popular swap trading strategies. It involves borrowing funds in a currency with a low-interest rate and investing the funds in a currency with a high interest rate. This is done to earn the difference in interest rates between the two currencies.
For example, if the interest rate in Japan is 0.1%, and the interest rate in the US is 2%, a trader can borrow in yen and invest in dollars. The trader will earn 1.9% (2% – 0.1%) annually.
The carry trade strategy requires a long-term outlook and an understanding of interest rate differentials. The trader needs to be able to predict the direction of interest rates and the movement of currencies.
Swap and Fly
For example, a trader can borrow in yen, invest in dollars, and then swap the investment for Australian dollars, which have a higher interest rate. The trader will earn the difference in interest rates between the three currencies.

Currency Futures Strategy
The currency futures strategy involves buying and selling currency futures contracts to earn a profit from the difference in the futures price and the spot price. The futures price is the expected price of a currency at a future date, while the spot price is the current price of the currency.
For example, a trader can buy a futures contract for the euro with a delivery date of six months in the future. If the spot price of the euro rises before the delivery date, the trader can sell the contract at a profit [11].
The currency futures strategy requires an understanding of the futures market and the factors that influence futures prices.
Long-Term and Short-Term Trading With Swaps
Swaps can be used for both long-term and short-term trading strategies. Long-term traders can use swaps to earn interest on their investments, while short-term traders can use swaps to take advantage of interest rate differentials in the short term.
For example, a long-term trader can invest in a currency with a high interest rate and hold the position for several months to earn interest on the investment. A short-term trader can buy a currency with a low interest rate, hold the position for a short time, and then sell the currency for a profit when the interest rate differential changes.
Foreign Exchange Swap Vs. Cross Currency Swap
Foreign exchange swaps and cross-currency swaps are both used in forex trading. A foreign exchange swap is a contract to exchange one currency for another currency at a specific time in the future. The exchange rate is agreed upon at the time the contract is made.
The Influence Of Crises On Swaps
Crises can have a significant impact on swaps. During times of economic instability, interest rates can fluctuate wildly, causing swap rates to change rapidly. This can create opportunities for traders to make a profit, but it can also create risks.
For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, central banks around the world lowered interest rates to stimulate economic growth. This caused the interest rate differential between currencies to narrow, reducing the potential profits from carry trade strategies [12].
However, crises can also create opportunities for traders to take advantage of interest rate differentials. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, central banks around the world lowered interest rates to support their economies. This created a wider interest rate differential between currencies, making carry trade strategies more profitable.
FAQ:
- Is swapping better than trading?
Swapping and trading are different financial instruments with different purposes. Swapping is an agreement between two parties to exchange financial instruments, cash flows, or liabilities for a predetermined period, while trading involves buying and selling assets in the financial markets to make a profit. Both swapping and trading have their advantages and disadvantages, and it depends on the individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy.

- When are swaps charged?
Swaps are charged when traders hold positions overnight, and the positions are not closed before the end of the trading day. The swap is charged as an interest rate differential between the two currencies in a currency pair. The swap rate can be positive or negative, depending on the currency pair and the interest rate differentials between the countries of the currencies in the pair.
- What is carry trade in swap strategy?
Carry trade is a swap strategy in forex trading where traders borrow a low-interest rate currency to buy a high-interest rate currency. The trader earns the interest rate differential between the two currencies while holding the position. Carry trade can be profitable if the interest rate differential is significant and the exchange rate remains stable.
- What Is a fixed-for-fixed swap?
A fixed-for-fixed swap is a financial agreement where two parties exchange fixed-rate payments in two different currencies. In a fixed-for-fixed swap, both parties agree to exchange a fixed amount of one currency for a fixed amount of another currency at a predetermined exchange rate.
- How does a Forex swap work?
A forex swap involves two parties exchanging cash flows based on an agreed-upon notional amount and exchange rate. The cash flows are based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded. One party pays the other party the interest rate differential, and the other party pays back the interest rate differential at a later date.
- What is a swap in Forex trading for example?
In forex trading, a swap is an interest rate differential between two currencies. For example, if a trader buys one lot of EUR/USD and holds the position overnight, the trader may be charged a swap fee if the interest rate differential between the euro and the dollar is negative. The swap fee is calculated based on the notional value of the trade and the interest rate differential between the two currencies.
- What is a swap fee in Forex?
A swap fee is a cost charged by brokers to traders who hold positions overnight. The swap fee is calculated as the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded and is charged for each day that the position is held open.
- How do I avoid swap fees in Forex?
Traders can avoid swap fees in forex trading by closing their positions before the end of the trading day. Another way to avoid swap fees is to trade with a forex broker that offers swap-free accounts. These accounts do not charge swap fees but may have other fees or restrictions.
- What is the benefit of a swap in Forex?
The benefit of a swap in forex trading is that it allows traders to hold positions overnight without having to close the positions and reopen them the next day. This can save time and reduce trading costs. Additionally, swaps can be used as a hedging strategy to reduce risk in a portfolio.
- Is swap better than exchange?
Swaps and exchanges are different financial instruments with different purposes, and they depend on the individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy. Swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows based on an interest rate differential, while an exchange is the buying and selling of assets in the financial markets. Both swaps and exchanges have their advantages and disadvantages.

- What is a swap on MT4?
A swap on MT4 is a fee charged by brokers to traders who hold positions overnight. The swap fee is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded and is charged for each day that the position is held open.
- What is a 3-day swap?
A 3-day swap is a type of swap agreement where the cash flows are exchanged for three days. This type of swap is commonly used in forex trading and is also known as a tom-next swap. The tom-next swap allows traders to extend the settlement date of a forex transaction by one day.
- Why are swaps risky?
Swaps can be risky because they involve counterparty risk, which is the risk that the other party to the swap agreement will default on their obligations. Additionally, swaps are subject to market risk, which is the risk that the value of the underlying assets or cash flows may fluctuate due to market conditions.
- Does a swap expire?
Swaps do not have a fixed expiration date but typically have a predetermined duration. The duration of a swap can be as short as one day or as long as several years. At the end of the swap period, the cash flows are settled between the parties.
- What is the difference between trade and swap?
Trading involves buying and selling assets in the financial markets to make a profit, while swapping involves exchanging cash flows, financial instruments, or liabilities with another party. Trading is typically done for short-term profits while swapping is a long-term financial strategy.
- What is an example of swap and drop?
Swap and drop is a trading strategy where a trader swaps two assets and then immediately sells one of the assets to realize a profit. For example, a trader could swap stock for a bond and then immediately sell the bond at a higher price to realize a profit.
- What are swap pips?
Swap pips are the number of pips that a trader earns or pays for holding a position overnight. The swap pips are calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded.
- What is the disadvantage of a swap?
The disadvantage of a swap is that it involves counterparty risk, which is the risk that the other party to the swap agreement will default on their obligations. Additionally, swaps can be subject to market risk, which is the risk that the value of the underlying assets or cash flows may fluctuate due to market conditions.
- Should I use a swap or not?
Whether or not to use a swap depends on the individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy. Swaps can be a useful financial tool for hedging risks or earning interest on cash balances, but they also involve counterparty and market risk.
- Why is the swap so high?
The swap rate can be high or low depending on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded. If the interest rate differential is high, the swap rate will also be high. Additionally, swaps can be affected by market conditions, such as changes in central bank policy or economic data releases.
- Are swap rates risk-free?
Swap rates are not risk-free, as they are subject to counterparty and market risk. The counterparty risk is the risk that the other party to the swap agreement will default on their obligations, while the market risk is the risk that the value of the underlying assets or cash flows may fluctuate due to market conditions.
- Who pays the swap rate?
The swap rate is paid by the trader who holds the position overnight. The swap rate is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded.
- What does the 10-year swap rate mean?
The 10-year swap rate is the interest rate differential between the 10-year government bonds of two countries. The 10-year swap rate is used as a benchmark in the financial markets to assess the creditworthiness of a country and to price a variety of financial instruments.
- What does the swap curve tell you?
The swap curve is a graphical representation of the interest rates that a borrower would pay to exchange one type of interest rate for another over different periods. The swap curve can provide information on the market’s expectations for future interest rates and can be used as a benchmark for pricing various financial instruments.
- What is the rule of swap?
The rule of swap is to pay or receive the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded for each day that the position is held open. The swap fee is typically charged at the end of each trading day.
- What happens when a swap fails?
When a swap fails, it means that one party to the swap agreement has failed to meet its obligations. This can result in financial losses for the other party, as well as legal action, to enforce the terms of the agreement.
- Why is swap negative?
A negative swap rate occurs when the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the forex pair being traded is negative. This means that the trader holding the position overnight will pay more interest on the borrowed currency than they will earn on the currency that they are holding. Negative swap rates can occur when interest rates in one country are lower than in another country.
Useful Video: What is SWAP in Forex Trading?
References:
- https://admiralmarkets.com/education/articles/forex-basics/forex-swap
- https://www.babypips.com/forexpedia/swap
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/foreign-currency-swaps.asp
- https://www.litefinance.org/blog/for-beginners/what-is-swap-in-forex-trading/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Foreign_exchange_swap
- https://www.dailyforex.com/forex-articles/2010/10/the-forex-swap/6209
- https://www.fpmarkets.com/education/forex-trading/what-is-swap-in-forex/
- https://capital.com/forex-swaps
- https://pepperstone.com/en/education/what-are-swaps-how-to-calculate-swaps/
- https://www.fxpro.com/help-section/traders-glossary/swap
- https://www.vantagemarkets.com/education/what-is-forex-swap-can-i-make-money-collecting-forex-swap/
- https://blog.roboforex.com/blog/2020/04/07/swaps-on-forex-examples-of-use/









Leave a Review